Numbers of Horned Lark (Eremophila alpestris) are increasing at high alpine and arctic breeding sites in Norway
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15845/on.v45i0.3640Keywords:
Mountain birds; breeding populations; winter habitatAbstract
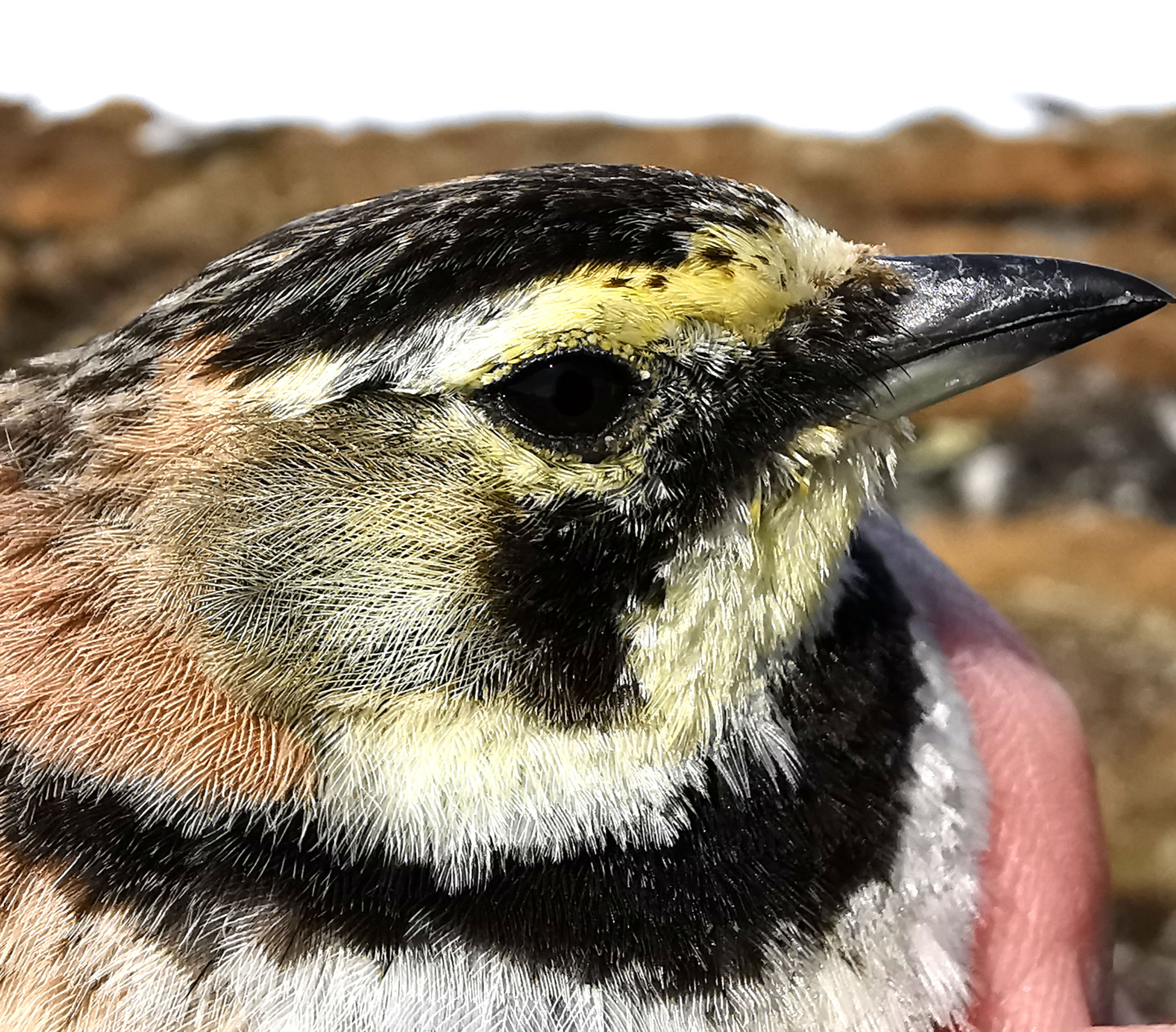
Cover photo: Female Horned Lark Eremophila alpestris. Photo: Terje Lislevand.
Strong declines in number of breeding Horned Larks Eremophila alpestris were reported from several Fennoscandian breeding grounds in the 1960s and 1970s. Counts from the species’ high alpine breeding grounds at Hardangervidda, southern Norway in the early 1980s and the first couple of decades in the 2000s, and from its arctic breeding grounds in the Varanger region, northern Norway in the period 1996-2021, show a reversal of the trend. The increase in numbers is suggested to have resulted primarily from recovery of nonbreeding habitat after cessation of extensive building of embankments to prevent flooding in the German Wadden Sea area, which is the main wintering area of Fennoscandian Horned Larks.

Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Ingvar Byrkjedal, Göran Högstedt

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles published prior to September 2020 are subject to the following terms: https://boap.uib.no/index.php/ornis/copyright